what are the three basic areas of a machine that require safeguarding
The point of operation That point where work is performed. Moving parts which are part of the machine or bigger system.

Chapter 1 Basics Of Machine Safeguarding
Safeguarding devices are controls or attachments that usually prevent inadvertent access by employees to hazardous machine areas when properly designed and installed.

. All components of the mechanical system which transmit energy to the part of the machine performing the work. All components of the mechanical system which transmit energy to the part of the machine performing the work. Cutting Shaping Boring Forming 2.
The point of operation from where all the work is performed. All components of the mechanical system which transmit energy to the part of the machine performing the work. Dangerous moving parts that need safeguarding are located in the three basic areas described below.
Following three basic areas require safeguarding. These components include flywheels. All machines consist of three fundamental areas the point of operation the power transmission device and the operating controls.
These include moving belts arms. Dangerous moving parts in three basic areas require machine safeguarding. There seem to be as many hazards created by moving machine parts as there are types of machines.
Point of operation guard requirements. Prevent contact machine guards must provide a physical barrier that prevents the operator from having any part of hisher body in the danger zone during the machines operating cycle. All components of the mechanical system which transmit energy to the part of the machine performing the work.
All machines consist of three fundamental areas. What are the three basic areas of a machine that require safeguarding. The point of operation.
Presence sensing pullback restraint safety controls and gates. The point where work is performed on the material such as cutting shaping boring or forming of stock. Dangerous moving parts in three basic areas require safeguarding.
The point of operation is the area on a machine where the work is performed. All components of the mechanical system which transmit energy to the part of the machine performing the work. Point of Operation Power Transmission Apparatus Other Moving Parts Question 2.
That point where work is performed on the material such as cutting shaping boring or forming of stock. Despite all machines having the same basic components their safeguarding needs widely differ due to varying physical characteristics and operator involvement. The point of operation.
That point where work is performed on the material such as cutting shaping boring or forming of stock. OSHA states that mechanical hazards are most likely to occur in three major areas. That point where work is performed on the material such as cutting shaping boring or forming of stock.
Machine safeguarding helps protect workers from preventable injuries in all three areas. These devices may perform one of several functions. That point where work is performed on the material such as cutting shaping boring or forming of stock.
Examples of guarding methods include. Dangerous moving parts in three basic areas require safeguarding. The point of operation the power transmission device and the operating controls.
These components include flywheels. Prevent entry of handsfingers into point of operation by reaching through over under or around guard. Dangerous moving parts in three basic areas require safeguarding.
Basics of Machine Safeguarding. Guards shall be affixed to the machine where possible and secured elsewhere if for any reason attachment to the machine is not possible to prevent access to the hazard from all accessible directions including front top bottom and backside. The point of operation.
Dangerous moving parts in three basic areas require safeguarding. The following pages address the general requirements for machinery set forth by. Safeguards are essential for protecting workers from needless and preventable injuries.
There are several mechanical motions that pose risks to workers. Be secured in place or otherwise be tamper proof machine guards must be secure and strong so that workers are not able to bypass remove or tamper with them. The point of operation.
The point of operation. Power transmission apparatus which feeds energy to machines. Crushed hands and arms severed fingers blindness -- the list of possible machinery-related injuries is as long as it is horrifying.
Any area containing components of a power transmission mechanical system which transmits energy to the. The point where work is performed on the material such as cutting shaping boring or forming of stock. Device that detects or prevents inadvertent access to a hazard.
All components of the mechanical system that transmit energy to the part of the machine performing the work. The purpose of machine guarding is to protect against and prevent injury from _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ Where Mechanical Hazards Occur Dangerous moving parts in threebasic areas require safeguarding. The point of operation.
The point of operation is the point where work is performed on the material such as cutting shaping boring or forming of stock.
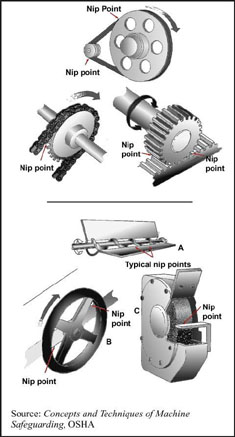
Etool Woodworking Machine Hazards Nip Points Occupational Safety And Health Administration

Oshacademy Course 154 Machine Safeguarding Basic Module 2

Chapter 1 Basics Of Machine Safeguarding

Chapter 1 Basics Of Machine Safeguarding

Machine Safeguarding 101 Rockford Systems Llc

Oshacademy Course 154 Machine Safeguarding Basic Module 1

Oshacademy Course 154 Machine Safeguarding Basic Module 1

Oshacademy Course 154 Machine Safeguarding Basic Module 1

Oshacademy Course 154 Machine Safeguarding Basic Module 1

Guards Methods Of Machine Guarding

Machine Guarding Four Types Of Guards Citations Fixed Interlocked Ppt Video Online Download





